Visualizing Pipelines - RefTrace v0.6.0
RefTrace is a linter that understands Nextflow pipelines.
This release introduces two new commands graph and info.
graph visualizes a pipeline.
info shows a pipeline as JSON.
Here’s rnaseq:
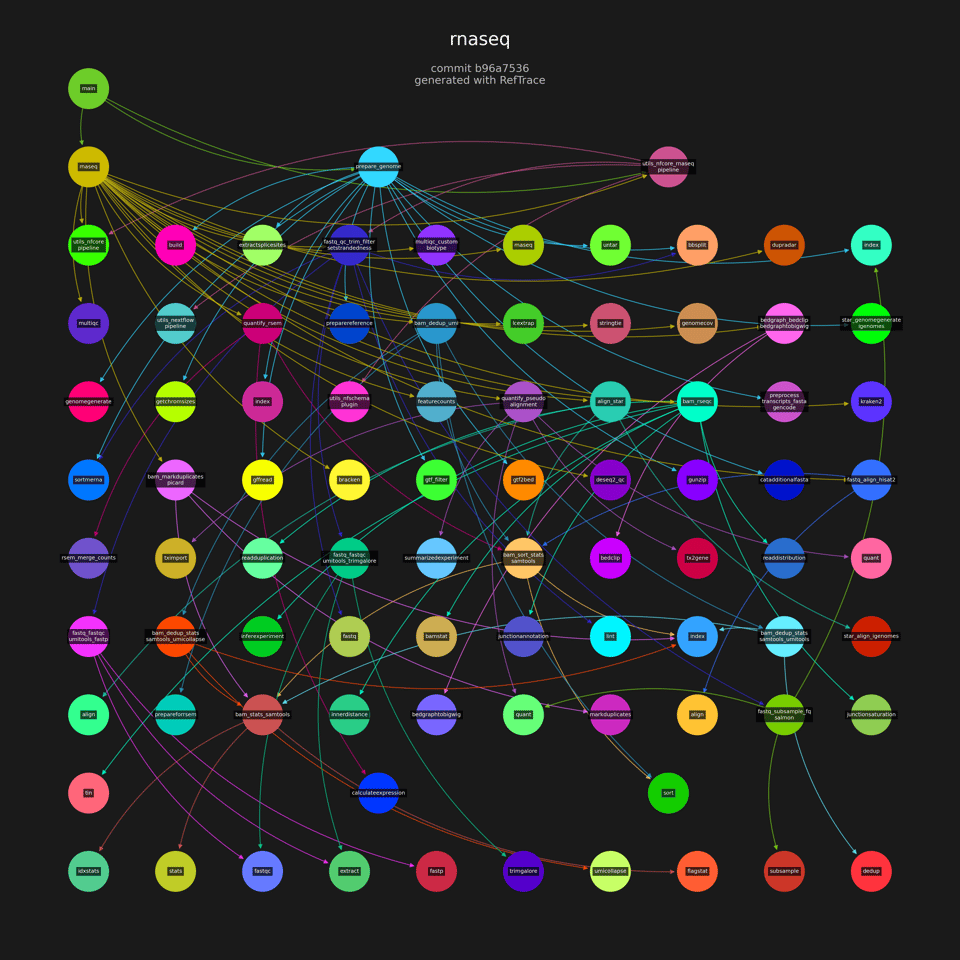
That image was produced with:
cd ~/rnaseq
pip install reftrace
reftrace graph
Each node is a Nextflow module. Each arrow corresponds to an include statement. You can see the main module includes three other modules:
include { RNASEQ } from './workflows/rnaseq'
include { PREPARE_GENOME } from './subworkflows/local/prepare_genome'
include { PIPELINE_INITIALISATION } from './subworkflows/local/utils_nfcore_rnaseq_pipeline'
include { PIPELINE_COMPLETION } from './subworkflows/local/utils_nfcore_rnaseq_pipeline'
include { checkMaxContigSize } from './subworkflows/local/utils_nfcore_rnaseq_pipeline'
I find it helpful to get a bird’s-eye view when working on a new pipeline.
Pipelines as JSON
Images are nice for people, but JSON is nicer for CI systems.
RefTrace’s info sub-command augments the graph view, helping answer questions about the codebase. Here’s what RefTrace outputs on a per-module basis:
$ reftrace info modules | jq '.modules | map(keys) | add | unique'
[
"dsl_version",
"includes",
"params",
"path",
"processes",
"workflows"
]
RefTrace can show reverse dependencies (i.e. where a module is used) with reftrace info rdeps. For instance:
{
"path": "modules/nf-core/dastool/fastatocontig2bin/main.nf",
"direct_rdeps": [
"subworkflows/local/binning_refinement.nf",
"subworkflows/local/tiara.nf"
],
"transitive_rdeps": [
"main.nf",
"subworkflows/local/domain_classification.nf",
"workflows/mag.nf"
]
}
As a codebase evolves, it can be easy to forget to delete old code. RefTrace finds unused modules:
$ reftrace info rdeps --isolated
Warning: Found isolated nodes:
modules/local/centrifuge.nf
modules/local/krona.nf
modules/local/nanolyse.nf
Python API
If you'd like to use the dependency graph from Python, you can:
>>> from reftrace.graph import make_graph
>>> import networkx as nx
>>> G = make_graph(".")
>>> nx.dag_longest_path(G)
['main.nf', 'workflows/rnaseq/main.nf', 'subworkflows/local/utils_nfcore_rnaseq_pipeline/main.nf', 'subworkflows/nf-core/fastq_qc_trim_filter_setstrandedness/main.nf', 'subworkflows/nf-core/fastq_subsample_fq_salmon/main.nf', 'modules/nf-core/salmon/index/main.nf']
Try It
RefTrace can be installed with pip install reftrace.
Check it out on GitHub or the website. Feel free to shoot me an email at andrew@reftrace.com with questions or feedback.