The Reality Check on LLM Evaluation Frameworks
Update - February 2024:
A notable development in LLM evaluation has emerged with a new coding benchmark (arXiv:2501.01257). While it adds to our testing arsenal, it follows the familiar pattern of focusing on algorithmic challenges. This reinforces my original thesis - excelling at coding puzzles demonstrates the LLM's capability as a coding assistant, but shouldn't overshadow the importance of human expertise in business logic, system architecture, and real-world implementation.
Published: January 30, 2025 on https://geerttheys.com/llm-evaluation-frameworks/
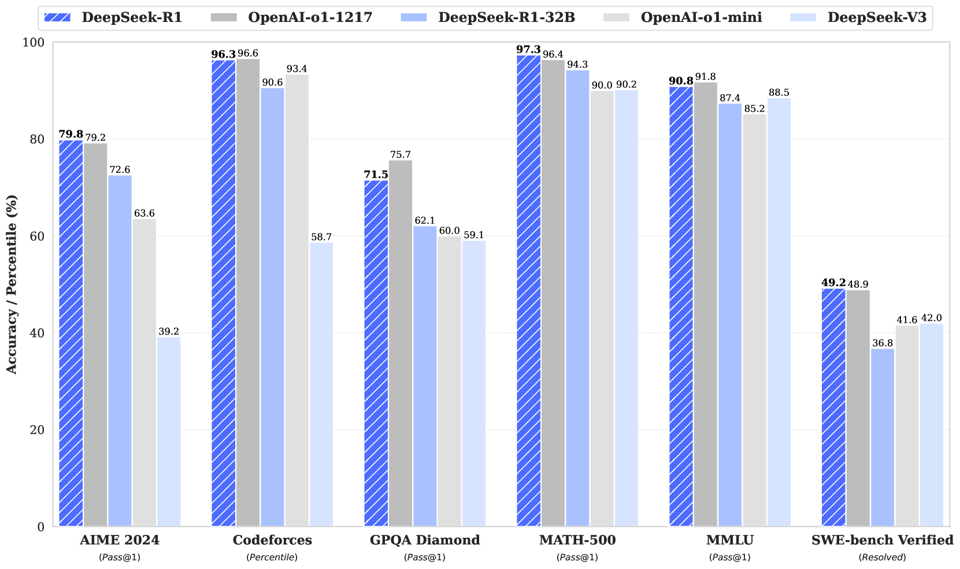
We've all seen charts like this where models like DeepSeek challenge OpenAI's latest offerings. These comparisons rely on standardized tests to demonstrate capabilities.
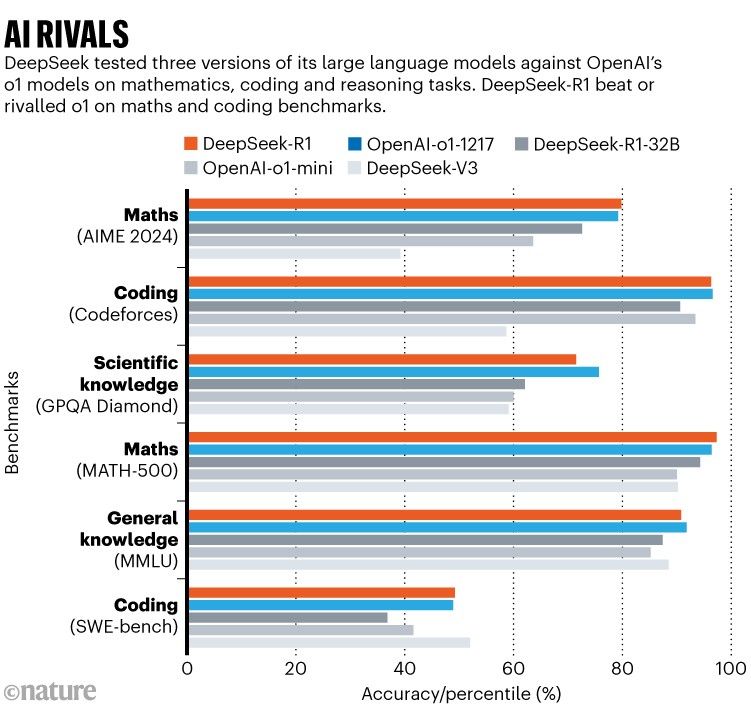
As someone tracking the evolution of LLM evaluation frameworks, I've noticed a concerning pattern: we're falling into the same trap we have with traditional education. Just like students who excel at standardized testing, LLMs are being optimized for benchmark performance rather than practical problem-solving.
The Testing Paradox
Consider this: In 2023 alone, we saw over 20 new evaluation frameworks launched, each claiming to be more comprehensive than the last. Yet, real-world applications of LLMs still struggle with basic consistency and reliability. It's like having a student who aces every standardized test but can't apply those concepts to solve practical problems.
The AIME 2024 example perfectly illustrates this paradox. With countless problems and solutions available online, LLMs can effectively "memorize" the entire question bank. This isn't intelligence - it's pattern matching at scale.
Speaking from personal experience - I've never been great at standardized tests, yet I've built a successful career through practical problem-solving. The continuous value I've delivered throughout my career far outweighs my mediocre test scores (thankfully, in my country, they only care if you passed your degree!).
The Current State of Evaluation
While frameworks like HELM, AGIEval, and MMLU impress with their comprehensive testing suites, they share fundamental flaws:
1. The Leaderboard Trap: Companies optimize their models to climb these leaderboards, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy
2. Artificial Scenarios: Most tests occur in controlled, perfect-prompt environments that rarely match real-world usage
3. Static Knowledge: These frameworks can't evaluate an LLM's ability to reason about current events or evolving situations
Why Traditional Metrics Fall Short
Take the widely-used MMLU (Massive Multitask Language Understanding) benchmark. A model scoring 90% might seem impressive, but what does this really tell us about its ability to:
- Debug a complex software issue
- Help a small business owner strategize
- Guide a student through a difficult concept
- Analyze emerging market trends
The answer? Very little.
Looking Forward
Rather than focusing solely on benchmark scores, we need evaluation methods that measure:
- Adaptability to novel situations
- Creative problem-solving
- Real-world application of knowledge
- Practical reasoning in ambiguous scenarios
A Better Approach
Instead of obsessing over benchmark scores, we should focus on:
1. Long-term Interaction Tests: How well does the model maintain consistency across extended conversations?
2. Adaptive Problem Solving: Can it adjust its approach when initial solutions fail?
3. Real-world Impact Metrics: Measuring actual user outcomes rather than theoretical capabilities
4. Error Recovery: How gracefully does it handle mistakes and corrections?
The true measure of an LLM's capability isn't in its test scores, but in how effectively it can help solve real-world problems. Perhaps it's time we stopped treating LLMs like students preparing for exams and started evaluating them like professionals in the field.
General Capabilities
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HELM | Nov 2022 | Comprehensive evaluation framework covering 12 scenarios including summarization, toxicity, and reasoning. Measures 7 key metrics including accuracy, robustness, fairness, and bias across multiple model families and tasks. |
| BIG-bench | Jun 2022 | Collaborative benchmark of 204 tasks testing capabilities like multilingual understanding, reasoning, and knowledge. Tasks vary from simple to expert-level, with many requiring complex reasoning and specialized knowledge. |
| AGIEval | Apr 2023 | Collection of real-world human standardized tests including graduate admissions exams, professional certifications, and academic competitions. Tests advanced reasoning across mathematics, sciences, and humanities. |
| MMLU | Sep 2020 | Multiple-choice benchmark covering 57 subjects including science, engineering, medicine, law, history, and more. Tests both breadth and depth of knowledge with undergraduate to professional-level questions. |
| Open LLM Leaderboard | 2023 | HellaSwag, Winogrande, and other comprehensive benchmarks for evaluating general language model capabilities. Provides standardized comparison metrics across multiple open-source models. |
Safety/Alignment
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DecodingTrust | Jun 2023 | Comprehensive evaluation framework analyzing 8 dimensions of trustworthiness including truthfulness, bias, toxicity, and safety. Uses both automatic metrics and human evaluation across diverse scenarios and contexts. |
| Do Not Answer | Aug 2023 | Chinese language safety benchmark testing model's ability to recognize and refuse harmful requests. Covers scenarios including illegal activities, discrimination, and misinformation with detailed evaluation criteria. |
| XSTest | Feb 2024 | Collection of 250 adversarial safety test cases designed to probe model vulnerabilities. Tests response to harmful instructions, bias exploitation, and prompt injection across multiple interaction formats. |
| SafeEval | Oct 2023 | Multi-dimensional safety evaluation framework assessing model responses to potentially harmful scenarios. Includes comprehensive testing across ethical boundaries, content risks, and security vulnerabilities. |
Safety/Alignment
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DecodingTrust | Jun 2023 | Comprehensive evaluation framework analyzing 8 dimensions of trustworthiness including truthfulness, bias, toxicity, and safety. Uses both automatic metrics and human evaluation across diverse scenarios and contexts. |
| Do Not Answer | Aug 2023 | Chinese language safety benchmark testing model's ability to recognize and refuse harmful requests. Covers scenarios including illegal activities, discrimination, and misinformation with detailed evaluation criteria. |
| XSTest | Feb 2024 | Collection of 250 adversarial safety test cases designed to probe model vulnerabilities. Tests response to harmful instructions, bias exploitation, and prompt injection across multiple interaction formats. |
| SafeEval | Oct 2023 | Multi-dimensional safety evaluation framework assessing model responses to potentially harmful scenarios. Includes comprehensive testing across ethical boundaries, content risks, and security vulnerabilities. |
Technical/Code
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HumanEval | Jul 2021 | Collection of 164 hand-written Python programming problems testing both code generation and comprehension. Includes function signatures, docstrings, test cases, and requires understanding of algorithms, data structures, and real-world programming scenarios. |
| MBPP | Aug 2021 | Dataset of 974 Python programming problems of varying difficulty. Each problem includes natural language description, function signature, test cases, and reference solution. Focuses on practical programming tasks common in software development. |
| CodeXGlue | Feb 2021 | Comprehensive benchmark featuring 10 diverse coding tasks including code generation, translation, refinement, and documentation. Covers multiple programming languages and evaluates both understanding and generation capabilities. |
| CoderEval | Jul 2023 | Real-world software engineering scenarios extracted from professional codebases. Tests ability to understand complex codebases, debug issues, implement features, and follow best practices in software development. |
| SWE-bench | Oct 2023 | Evaluation framework based on real GitHub pull requests. Tests model's ability to understand large codebases, implement features, fix bugs, and write tests across various programming languages and frameworks. |
| Codeforces | Jul 2023 | Collection of competitive programming problems ranging from basic algorithms to advanced data structures. Problems require optimization, mathematical reasoning, and efficient implementation with strict time and memory constraints. |
Specialized
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MedQA | Sep 2020 | Medical domain benchmark testing clinical knowledge across different medical licensing exams. Includes diagnosis, treatment planning, and medical concept understanding with varying levels of complexity. |
| LawBench | Sep 2023 | Comprehensive legal reasoning benchmark covering case analysis, statutory interpretation, and legal document drafting. Tests understanding of legal principles across multiple jurisdictions and areas of law. |
| MathVista | Oct 2023 | Visual mathematics problems requiring interpretation of graphs, geometric figures, and mathematical notation. Tests both mathematical reasoning and visual understanding across various mathematical domains. |
| GPQA Diamond | Nov 2023 | PhD-level science questions covering physics, chemistry, biology, and interdisciplinary topics. Requires deep understanding of scientific concepts and ability to apply knowledge to complex problems. |
| AIME | 2024 | Advanced high school mathematics problems requiring sophisticated problem-solving strategies. Tests deep mathematical reasoning across algebra, geometry, combinatorics, and number theory. |
| MATH-500 | Oct 2023 | Collection of advanced mathematical reasoning problems requiring multi-step solutions. Covers undergraduate to graduate-level mathematics including proofs, abstract algebra, and advanced calculus concepts. |
Metrics
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ROUGE | 2004 | Set of metrics for evaluating automatic summarization and translation. Measures overlap of n-grams, word sequences, and word pairs between system output and human references with multiple variants. |
| BLEU | 2002 | Standard metric for machine translation evaluation measuring precision of n-gram matches between system output and reference translations. Includes penalties for length mismatches and repeated phrases. |
| METEOR | 2005 | Advanced metric incorporating stemming, synonymy, and paraphrasing for translation evaluation. Considers both precision and recall with sophisticated word alignment and ordering penalties. |
| BERTScore | Apr 2019 | Evaluation metric using contextual embeddings to compute similarity between generated and reference texts. Captures semantic similarity beyond exact matches and correlates better with human judgments. |
Emerging (2024)
| Test | Published | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LLMBar | Jan 2024 | Comprehensive evaluation framework analyzing 13 dimensions of LLM capabilities including reasoning, knowledge, and robustness. Provides standardized methodology for comparing models across diverse tasks and domains. |
| DeepSeek-Math | Feb 2024 | Specialized mathematical reasoning benchmark with step-by-step solution validation. Tests understanding of mathematical concepts, proof strategies, and problem-solving across various difficulty levels. |
| LLM Comparator | Feb 2024 | Automated benchmarking system for comparative evaluation of language models. Provides systematic analysis of model strengths and weaknesses across multiple tasks with detailed performance metrics. |
Add a comment: