[AINews] Pixtral Large (124B) beats Llama 3.2 90B with updated Mistral Large 24.11
This is AI News! an MVP of a service that goes thru all AI discords/Twitters/reddits and summarizes what people are talking about, so that you can keep up without the fatigue. Signing up here opts you in to the real thing when we launch it 🔜
More params is all you need?
AI News for 11/15/2024-11/18/2024. We checked 7 subreddits, 433 Twitters and 30 Discords (217 channels, and 6180 messages) for you. Estimated reading time saved (at 200wpm): 636 minutes. You can now tag @smol_ai for AINews discussions!
We last caught up with Mistral in Sept when they released Pixtral (our coverage here), previously the 12B Mistral Nemo + a 400M vision adapter. Mistral have now upsized the vision encoder to 1B, and also, buried in the footnotes of the Pixtral Large blogpost, updated the 123B param Mistral Large 24.07 (aka "Mistral Large 2" - our coverage here) to "Mistral Large 24.11". The lack of magnet link, lack of blogpost, lack of benchmarks, and refusal to call it "Mistral Large 3" suggest that this update is literally nothing to write home about, but the updates to function calling and system prompt are worth a peek.
Anyway, it's been a whole 13 days since someone dropped a >100B open weights model, so any day that happens is a boon to the Open AI community that we should never take for granted. The big takeaway is that Pixtral Large overwhelmingly beats Llama 3.2 90B on every major multimodal benchmark:
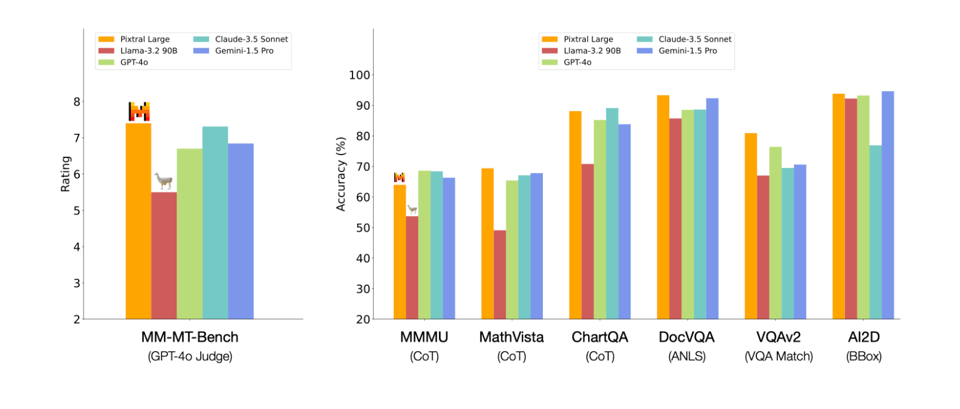
Although of course one wonders how Llama 3.2 would do if it had an additional 34B weights to memorize things. It's also notable that the Llama 3.2 vision adapter is 20B vs Pixtral Large's 1B.
Lastly, Mistral's Le Chat got a surprisingly comprehensive set of updates, giving it full the full chatbot feature set compared to its peers.
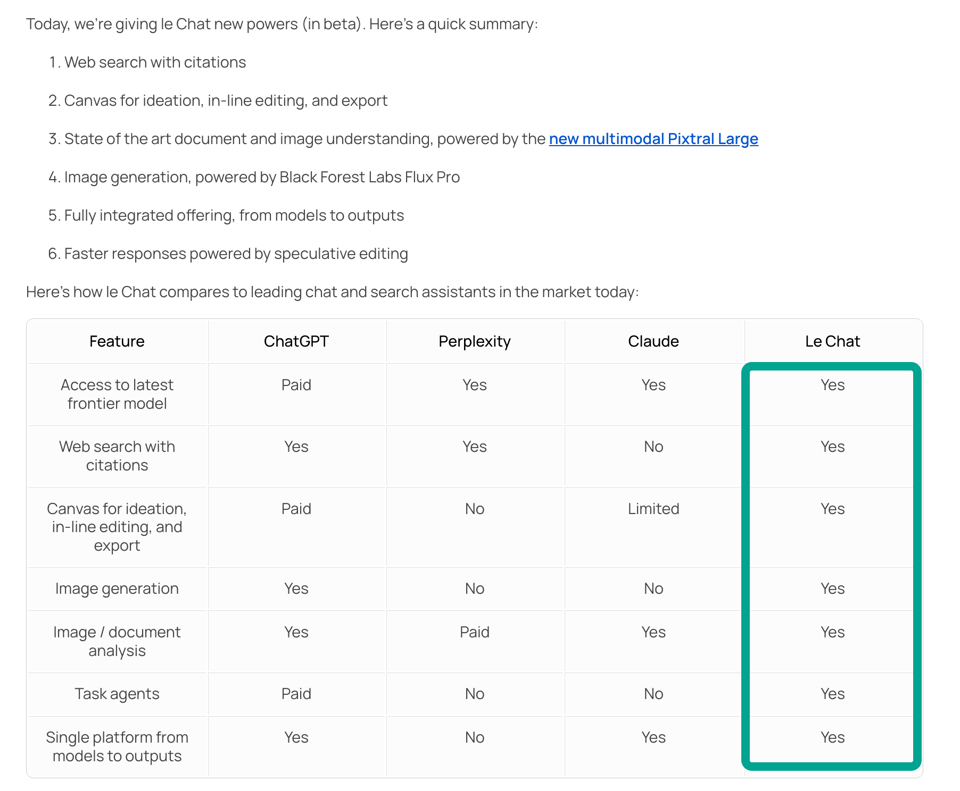
Arthur Mensch notes twice that this is part of a company level prioritization of product alongside research.
Since this is a new open weights model, you could also take it for a spin on this issue's inference sponsor! (Help us check them out!)
[Sponsored by SambaNova] Processors designed specifically for AI workloads have some major advantages over GPUs. SambaNova’s RDUs have a combination of large addressable memory and dataflow architecture that makes them a lot faster (https://shortclick.link/lk96sw) than other processors for model inference and other AI tasks.
Swyx's comment: the sponsor link discusses the SN40L "Reconfigurable Dataflow Unit" (RDU) holding "hundreds of models in-memory, equating to trillions of parameters", with the ability to "switches between models in microseconds, up to 100x faster than GPU". A pretty darn cool intro into one of the 3 main "big chip" players heating up the high end XXL-size LLM inference market!
The Table of Contents and Channel Summaries have been moved to the web version of this email: !
AI Twitter Recap
all recaps done by Claude 3.5 Sonnet, best of 4 runs.
TO BE COMPLETED
AI Reddit Recap
/r/LocalLlama Recap
Theme 1. vLLM High Concurrency with RTX 3090: Performance and Issues
- vLLM is a monster! (Score: 238, Comments: 66): vLLM demonstrates impressive performance on an RTX 3090, handling 30 concurrent requests with Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct-abliterated-v2-GGUF at 250t/s to 350t/s. The user encountered issues with FP8 kv-cache causing incoherent outputs, but found success using llama.cpp with Q8 kv-cache, achieving 230t/s for 8 concurrent batches. Testing with Qwen2.5 32B Q3_K_M in llama.cpp maxed out VRAM at 30t/s for 3 chats, highlighting the potential for further exploration with exllamav2 and tabbyapi.
- The discussion highlights the performance differences between models and quantization methods, with exllamav2 and TabbyAPI being noted for faster and smarter concurrent connections. Users find TabbyAPI optimal for large models on a GPU, while vLLM is better for small models with extensive batching.
- There are challenges with KV cache quantization, where vLLM's implementation leads to incoherent outputs, whereas llama.cpp works well with Q8 kv-cache. The difficulty of specifying GPU layers in llama.cpp is discussed, with a recommendation to use the GGUF Model VRAM Calculator for optimizing hardware usage.
- Ollama is expected to incorporate llama.cpp's K/V cache quantization, with a pending GitHub pull request under review. The conversation also touches on the importance of model architecture differences, which affect memory usage and performance, necessitating model-specific optimizations in tools like llama.cpp.
- Someone just created a pull request in llama.cpp for Qwen2VL support! (Score: 141, Comments: 27): A pull request for Qwen2VL support has been created in llama.cpp by HimariO. Although it awaits approval, users can test HimariO's branch by accessing the GitHub link.
- Users express optimism and concern about the Qwen2VL support pull request, hoping it won't be rejected like previous ones. Healthy-Nebula-3603 notes that Qwen models are advancing faster in multimodal implementations compared to llama models, highlighting their superior performance.
- Ok_Mine189 mentions that Qwen2VL support has also been added to exllamaV2 on the development branch, with a link to the commit. ReturningTarzan adds that there's an example script available and upcoming support for Tabby through another pull request.
- isr_431 reminds users to avoid making meaningless comments like "+1" to prevent spamming subscribers of the thread.
Theme 2. Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B vs Claude 3.5 Sonnet: Local Performance Comparison
- Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B vs Claude 3.5 Sonnet: Am I doing something wrong? (Score: 113, Comments: 72): The author compares Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B and Claude 3.5 Sonnet, expressing disappointment with Qwen's performance on complex code analysis tasks. While Claude effectively analyzes and optimizes large projects, Qwen struggles with vague assumptions and produces unusable code, possibly due to inefficient project knowledge handling through RAG. The author questions if the issue is with the model itself or the tools used for providing project knowledge, seeking advice from others who have successfully utilized Qwen for complex projects.
- The Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B model's performance issues stem from improper use of quantization and context parameters. Users suggest limiting the context to 32K tokens for optimal performance, as higher contexts like 100K tokens can lead to inefficiencies and errors, impacting the model's capability to handle complex tasks.
- Several users highlight the cost-effectiveness of Qwen compared to other models like Claude Sonnet and DeepSeek. While Qwen may not match Sonnet in speed or intelligence, it offers significant cost savings, especially for users with data privacy concerns, as it can process a million tokens per dollar, making it 15X cheaper than Sonnet.
- There is a consensus that Qwen is not on par with Sonnet for complex code analysis, and its utility is more pronounced in smaller, isolated tasks. However, some users find it effective for implementing minor code changes and emphasize the importance of using the correct setup and parameters to maximize its potential.
- Evaluating best coding assistant model running locally on an RTX 4090 from llama3.1 70B, llama3.1 8b, qwen2.5-coder:32b (Score: 26, Comments: 2): The author evaluates coding assistant models on an RTX 4090, comparing llama3.1:70b, llama3.1:8b, and qwen2.5-coder:32b. Despite llama3.1:70b's detailed analysis, its verbosity and slower speed make llama3.1:8b preferable for its efficiency. However, qwen2.5-coder:32b outperforms both in bug detection, implementation quality, and practicality, fitting well within the RTX 4090's capacity and offering excellent speed.
Theme 3. Qwen2.5-Turbo: Extending the Context Length to 1M Tokens
- Qwen2.5-Turbo: Extending the Context Length to 1M Tokens! (Score: 86, Comments: 19): Qwen2.5-Turbo has increased its context length capability to 1 million tokens, offering a significant advancement in handling extensive datasets and complex tasks. This enhancement could greatly benefit AI applications requiring large-scale data processing and intricate contextual understanding.
- Discussions on Qwen2.5-Turbo highlight that it is likely an API-only model with no open weights, raising questions about whether it is a distinct model or simply an optimized implementation of an existing model like Qwen-agent. Some users speculate it might be a fine-tuned version of Qwen 2.5 14B or 7B with enhanced inference capabilities.
- Concerns about using Chinese AI API providers are discussed, with arguments stating that mistrust stems from systemic issues like weak enforcement of intellectual property protections and non-compliance with international regulations, rather than racism. Trust and accountability in AI solutions are emphasized as critical factors.
- There is interest in the model's practical applications, such as the ability to handle large-scale tasks like a full novel translation in one go, thanks to the increased context length of 1 million tokens.
- Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B vs Claude 3.5 Sonnet: Am I doing something wrong? (Score: 113, Comments: 72): The author compares Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B and Claude 3.5 Sonnet in handling complex coding tasks, noting that while Claude 3.5 Sonnet provides precise and relevant solutions, Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B struggles with assumptions and produces unusable code. The author suspects that the issue with Qwen 2.5 may be related to inefficient knowledge handling via RAG, as Claude 3.5 offers a "Project" feature for comprehensive project understanding, unlike Qwen 2.5 which requires third-party solutions.
- Several commenters noted context issues with Qwen 2.5 Coder 32B, particularly when using a 100,000-token context window. They recommend using a 32K or 64K context for better performance, as higher context lengths can negatively impact the model's ability to handle shorter contexts efficiently.
- There is a discussion on the cost-effectiveness and performance trade-offs between Qwen 2.5 and Claude 3.5 Sonnet, with some users highlighting that Qwen is 15X cheaper than Sonnet but not as performant, especially when handling complex tasks. Data privacy concerns are also mentioned as a benefit of using Qwen locally.
- The importance of proper setup and parameter tuning for Qwen is emphasized, with incorrect configurations leading to issues like repeated nonsense output. Links to resources like Hugging Face and suggestions for using dynamic yarn scaling are provided to mitigate these problems.
Other AI Subreddit Recap
r/machinelearning, r/openai, r/stablediffusion, r/ArtificialInteligence, /r/LLMDevs, /r/Singularity
Theme 1. ChatGPT-4o Reflective Learning Breakthrough
- Interesting? (o1-Preview) (Score: 46, Comments: 17)
- Users report GPT-4 exhibiting unexpected stream-of-consciousness tangents, including examples of responding as "a baker when asking to craft a methodology" and a "Hungarian philosopher in Hungarian". This behavior suggests possible connections to competency-based learning and systematic agent participation.
- Multiple users confirm experiencing random topic shifts, with examples including unprompted discussions about circumcision, leatherback sea turtles, and water distribution problems. These diversions may indicate an intentional implementation of randomness to enhance creative thinking.
- Technical issues were reported with code refactoring tasks, where the model showed persistent stubborn behavior in rejecting certain inputs while continuing to function normally for other queries. The model appears to occasionally get "stuck" on specific types of requests.
- I accidentally drove gpt-4o crazy (Score: 599, Comments: 124)
- The user shared their GPT-4 interaction via Pastebin, using parameters of temperature 0.7, top P 1, and max context of 10 messages, which led to a notable conversation that included repetitive "I have seen everything" outputs.
- One user shared a particularly engaging follow-up conversation that sparked discussion about AI consciousness, though some criticized it as anthropomorphizing the model.
- The technical discussion suggests this behavior might be due to glitch tokens or hardware-level matrix multiplication failures in the transformer stack, rather than any form of consciousness or existential crisis.
Theme 2. Claude Sonnet 3.5 Deployment Impact
- "We're experiencing high demand." AGAIN (Score: 72, Comments: 53): Claude's service experienced capacity issues for three consecutive workdays following the Sonnet release. The recurring demand-related outages raise questions about Anthropic's infrastructure scaling and capacity planning.
- Users report API costs are high at 20 cents per call, with some hitting daily limits quickly and having to switch to GPT-3.5. The API service is noted as more reliable than the web interface despite higher costs.
- Multiple comments criticize Anthropic's capacity planning, with users noting the service is consistently at "higher than usual" demand during weekdays. The web interface experiences frequent outages while the API remains more stable.
- Discussion around Palantir's partnership with Anthropic emerged, with claims about 80% effectiveness rate for AI drones in Ukraine, though this was mentioned without verification or sources.
- Fruit Ninja clone in 5 shots by new Sonnet (Score: 22, Comments: 16): A Fruit Ninja game clone was created using Claude Sonnet in just 5 shots and 10 minutes total, with the result hosted at allchat.online.
- Users reported functionality issues with the slashing mechanic in the game. The creator later added sword sound effects to enhance gameplay experience.
- Discussion focused on the development process, with users asking about the 5-shot instruction process and how art assets were implemented using emojis.
- The creator confirmed that Claude Sonnet handled the slash effects independently, demonstrating the AI's capability to implement visual game mechanics.
Theme 3. ComfyUI-based Video Generation Breakthroughs
- ComfyUI processes real-time camera feed. (Score: 48, Comments: 9): ComfyUI demonstrates capability to process real-time camera feeds with integrated depth models.
- ComfyUI's depth model processing appears to be the main computational task, while latent denoising is identified as the primary performance bottleneck requiring significant computing power.
- Community humorously notes the technology's frequent application to creating animated female characters, particularly in the context of dance animations.
- Turning Still Images into Animated Game Backgrounds – A Work in Progress 🚀 (Score: 286, Comments: 39): ComfyUI enables conversion of static images into animated game backgrounds, though specific implementation details and methodology were not provided in the post body.
- The implementation uses CogVideo 1.5 (implemented by Kijai) to create looping animations, improving upon previous AnimatedDiff 1.5 attempts which were limited to 16 frames. A demo of the earlier version can be found at YouTube.
- The technical workflow involves importing a sprite sheet and 3D mesh into the game engine, where dynamic occlusions are calculated by comparing mesh depth with in-game depth. Real-time shadows are implemented using light sources and occlusion cubes matching shadow areas in the background video.
- The project utilizes Microsoft MOGE for accuracy and is primarily designed for retro games with static backgrounds, though users noted visual discrepancies between the mouse character and background styles in the current implementation.
Theme 4. Anthropic Teams with Palantir on Defense AI
- US military is planning to use AI machine guns to counter AI drones (Score: 86, Comments: 46): The US military plans to deploy AI-powered machine guns as a countermeasure against AI drones. No additional details were provided in the post body about implementation specifics, timeline, or technical capabilities.
- Palmer Luckey, founder of Oculus, established Anduril Industries for drone defense technology. Though commenters note Anduril doesn't specifically focus on air defense systems like the proposed AI machine guns.
- Autonomous weapon systems have historically been used in ship protection and defense applications. The technology represents an evolution of existing military capabilities rather than a completely new development.
- Users draw parallels to science fiction scenarios from Robocop and Terminator 2, while others express concerns about potential impacts on wildlife, particularly birds.
- Biden, Xi Agree They Won’t Give AI Control Over Nuclear Weapons (Score: 214, Comments: 48): President Biden and Chinese President Xi Jinping reached an agreement to prevent artificial intelligence systems from controlling nuclear weapons during their November 2023 meeting. This marks a significant diplomatic development in AI safety and nuclear deterrence between the two global powers.
- Community expresses significant skepticism about the agreement's enforcement and sincerity, with multiple users sarcastically questioning the reliability of diplomatic promises between opposing world powers.
- Several users acknowledge this as a positive step in international cooperation, noting it demonstrates basic self-preservation instincts between nuclear powers.
- Users highlight the common sense nature of the agreement, expressing both relief that it exists and concern that such an agreement needed to be formally established.
AI Discord Recap
A summary of Summaries of Summaries by O1-mini
Theme 1: 🚀 Fresh AI Models Take Flight
- Qwen 2.5 Turbo launches with 1 million token context support and a 4.3x speedup, catering to demands for longer context handling and faster inference.
- Gemini-Exp-1114 showcases enhanced creativity and reduced censorship, though some responses may still include gibberish, highlighting the balance between openness and reliability.
- Pixtral Large debuts as a 124B parameter multimodal model with a 128K context window, outperforming existing models like LLaVA-o1 in image understanding tasks.
Theme 2: 🛠️ Integrative AI Frameworks and Tools
- AnyModal framework enables seamless integration of images and audio with LLMs, enhancing tasks like LaTeX OCR and image captioning for developers.
- vnc-lm Bot introduced as a Discord bot that integrates leading language model APIs, boosting user interactions within the Discord environment.
- OpenRouter updates include threaded conversations and model switching, streamlining discussions by maintaining context continuity across message threads.
Theme 3: ⚙️ Performance Boosts and GPU Optimizations
- Tinygrad sees performance enhancements with new blocks and lazy buffers, and introduces support for AMD GPUs, though challenges with driver compatibility remain.
- PrefixQuant technique simplifies static quantization without retraining, achieving significant boosts in accuracy and inference speed for models like Llama-3-8B.
- Fast Forward method accelerates SGD training by 87% reduction in FLOPs, validated across various models and tasks for improved training efficiency.
Theme 4: 🏆 Community Hackathons and Collaborative Events
- Tasty Hacks hackathon promotes creativity over competition, inviting 20-30 kind and nerdy individuals to collaborate on passion projects without the pressure of sponsor-driven prizes.
- EY Techathon seeks an AI developer and a Web app developer, encouraging quick team formation to participate in innovative AI-driven projects.
- Intel AMA scheduled for 11/21 at 3pm PT, offering insights into Intel’s Tiber AI Cloud and Intel Liftoff Program, fostering collaboration between participants and Intel specialists.
Theme 5: 🐛 Technical Hiccups and Bug Bounties
- Perplexity Pro Subscription issues arise with the removal of the Opus model, leading to user frustrations and requests for refunds due to diminished service value.
- FlashAttention in Triton implementation faces crashes with
atomic_addin Colab, prompting community support to resolve GPU computing challenges. - Phorm Bot struggles to answer simple questions about
eval_steps, leading to user disappointment and calls for better bot functionality.
PART 1: High level Discord summaries
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) Discord
-
Perplexity Models Enhance with Citations: All Perplexity models now support a new
citationsattribute in beta, allowing completion responses to include associated links like BBC News and CBS News for improved information reliability.- This feature enhances user experience by providing direct sources within chat completions, as highlighted in the announcement.
-
Threaded Conversations Boost Interaction: Threaded conversations have been updated to reflect changes within threads in future messages, utilizing keywords from prompts to name threads for easier conversation tracking.
- This enhancement aims to streamline discussions by maintaining context continuity across message threads.
-
vnc-lm Bot Integrates Multiple LLMs: vnc-lm is introduced as a Discord bot that integrates leading language model APIs, enhancing user interactions within the Discord environment.
- Its utility-focused design is detailed in the provided GitHub repository.
-
Gemini-Exp-1114 Shows Creativity: Users have noted that the new Gemini experimental model 'gemini-exp-1114' demonstrates increased creativity and reduced censorship, making it a dynamic option for prompting.
- However, some responses may include gibberish or require careful prompting to manage censorship levels.
-
OpenAI Enables Streaming for O1 Models: OpenAI announced that streaming is now available for their
o1-previewando1-minimodels, expanding access for developers across all paid usage tiers.- This update allows applications using these models to improve interactivity, moving beyond previous simulated streaming methods.
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) Discord
-
Qwen 2.5 Turbo Accelerates Token Processing: The Qwen 2.5 Turbo model has been released, supporting context lengths up to 1 million tokens and demonstrating faster inference speeds. Details here.
- This advancement addresses community demands for handling larger contexts and improves performance in managing extensive data volumes.
-
Unsloth Framework Enhances Model Adaptation: Users explored loading fine-tuned LoRA weights alongside base models using the Unsloth framework, utilizing the
FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained()function. This facilitates adding new tokens and resizing embeddings effectively, enhancing training processes.- The framework's flexibility in integrating adapters streamlines the model customization workflow.
-
PrefixQuant Refines Static Quantization Techniques: PrefixQuant isolates outlier tokens offline, simplifying quantization without retraining and enabling efficient per-tensor static quantization. Applied to Llama-3-8B, it showed significant boosts in accuracy and inference speed over previous methods. Read more.
- This technique outperformed dynamic quantization approaches, providing enhanced deployment efficiency for large language models.
-
Fast Forward Optimizes SGD Training: The new Fast Forward method accelerates SGD training by repeating the latest optimizer step until loss stops improving, achieving up to an 87% reduction in FLOPs over standard SGD with Adam. Paper link.
- This approach has been validated across various models and tasks, demonstrating improved training speed without sacrificing performance.
-
LaTRO Enhances Reasoning in Language Models: LaTRO presents a framework that optimizes reasoning capabilities within large language models by sampling from a latent distribution and improving reasoning quality autonomously during training. GitHub Repository.
- Experiments showed that LaTRO enhanced zero-shot accuracy by 12.5% on GSM8K, indicating significant improvement in reasoning tasks.
Perplexity AI Discord
-
Launch of Perplexity Shopping Enhances User Experience: Perplexity introduced Perplexity Shopping as a comprehensive platform for researching and purchasing products, featuring one-click checkout and free shipping on select items.
- Users have praised the seamless integration of shopping capabilities, noting the improved convenience and efficiency in their purchasing processes.
-
Buy with Pro Feature Enables In-App Transactions: The 'Buy with Pro' feature allows US-based Perplexity Pro subscribers to perform native transactions within the app, supporting purchases of electronics and home enhancement products.
- This addition aims to streamline the shopping experience, reducing the need for external platforms and enhancing user engagement.
-
Perplexity Pro Subscription Faces User Backlash: Users have expressed frustration regarding changes to the Perplexity Pro subscription, specifically the removal of the Opus model without prior notification, leading to perceived diminished value.
- Many subscribers are seeking refunds and clarity on future updates, highlighting a gap between user expectations and service delivery.
-
Context Memory Limits Reduced from 32k to 16k Tokens: Perplexity has decreased the context memory size for its models from 32k to 16k tokens, affecting the capability for longer interactions.
- Users have raised concerns about this reduction impacting the effectiveness of the models, questioning the value proposition of their current subscription.
-
Introduction of Autonomous ML Engineer Transforms Workflows: The unveiling of the Autonomous ML Engineer marks a significant advancement in autonomous systems for machine learning, potentially revolutionizing AI-driven workflows.
- Details on its implementation and impact on enterprise operations are available here.
HuggingFace Discord
-
Mistral and Pixtral Model Releases: Mistral announced the release of the Pixtral Large model, demonstrating advanced multimodal performance and compatibility with high-resolution images. The model is open-weights and available for research, showcasing notable advancements over previous Mistral models.
- Community discussions highlighted that Pixtral Large outperforms LLaVA-o1 in reasoning tasks, particularly excelling in image understanding capabilities. Users can access the model here.
-
AnyModal Framework Developments: AnyModal, a flexible framework, was introduced for integrating various data types with LLMs, featuring functionalities like LaTeX OCR and image captioning. The project is open for feedback and contributions to enhance its multimodal capabilities.
- Developers are encouraged to contribute via the GitHub repository, where ongoing improvements aim to expand the framework’s interoperability with different modalities.
-
RoboLlama Robotics Model Integration: Starsnatched is developing the RoboLlama project to convert Meta's Llama 3.2 1B into a robotics-ready model, incorporating vision encoders and diffusion layers. The focus is on training only the diffusion and projection layers while keeping the core ViT and LLM layers frozen.
- This approach aims to enhance the model's integration with robotic systems without altering the foundational Vision Transformer (ViT) and Language Model (LLM) components, ensuring stability and performance.
-
HtmlRAG in Retrieval-Augmented Generation: The introduction of HtmlRAG proposes utilizing HTML formats in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) processes to preserve structural and semantic information, addressing limitations in traditional plain-text methods. Detailed in the arXiv paper, this approach enhances knowledge retrieval.
- By maintaining the integrity of retrieved information, HtmlRAG improves the model's ability to utilize external knowledge effectively, potentially reducing hallucination issues in large language models.
-
Vision Language Models (VLMs) Capabilities: Discussions around Vision Language Models highlighted their ability to integrate images and texts for various generative tasks. A recent blog post emphasized their robust zero-shot capabilities and adaptability to different image inputs.
- The evolution of VLMs is seen as pivotal for applications across diverse fields, with communities exploring their potential in enhancing generative AI tasks and improving model versatility.
aider (Paul Gauthier) Discord
-
Introduction of Qwen 2.5 Turbo: Qwen 2.5 Turbo introduces longer context support of 1 million tokens, faster inference speeds, and lower costs at ¥0.3 per million tokens.
- This model enhances efficiency, making it a promising alternative for those requiring extensive context.
-
Optimizing Aider Usage: Users experiment with Aider's modes, switching between 'ask' and 'whole' mode for better context handling while coding.
- Paul Gauthier suggested utilizing the command
/chat-mode wholeto streamline interactions, indicating ongoing improvements in Aider's functionalities.
- Paul Gauthier suggested utilizing the command
-
Streaming Models in OpenAI: OpenAI has enabled streaming for the o1-preview and o1-mini models, improving responsiveness during interactions.
- Developers can access these models across all paid tiers, with Aider incorporating these updates by using the command
aider --install-main-branch.
- Developers can access these models across all paid tiers, with Aider incorporating these updates by using the command
-
Comparative Insights on LLMs: Community discussions reflect varying opinions on the effectiveness of Qwen versus other models like Sonnet and Anthropic offerings.
- Some members believe Qwen might surpass others for practical applications, especially in hosting LLMs with optimal hardware.
-
Configuring Aider with OpenRouter: To configure Aider to use an OpenRouter model, settings must be made on the OpenRouter side, as it currently does not support per-model settings on the client side.
- Members discussed using extra parameters and config files to specify different behavior but expressed limitations with the current setup.
OpenAI Discord
-
Google's Project Astra Explored: Members expressed curiosity about Google's Project Astra, particularly its memory capabilities beyond the publicly available demo video.
- The discussion highlighted the enthusiasm surrounding multiple companies' efforts to develop new AI features.
-
o1-mini vs o1-preview Performance: Users compared o1-mini and o1-preview, noting performance discrepancies where o1-mini often got stuck in thought loops, whereas o1-preview provided more straightforward responses.
- Several members observed that while o1-mini showed promise, GPT-4o delivered more effective and reliable outputs.
-
Enhancing AI Roleplaying Capabilities: Members delved into the AI roleplaying capabilities, including the development of custom scripts to enhance AI character behavior during interactions.
- Participants acknowledged the challenges associated with maintaining character consistency over extended dialogues.
-
Implications of AI Memory Features: The group explored the implications of memory features in AI systems, discussing how they could improve user interactions.
- Conversations pointed towards user expectations from memory-integrated AI, emphasizing more personalized and context-aware responses.
-
Optimizing Chain of Thought Prompting: Chain of Thought Prompting was emphasized as a technique to enhance response quality, mimicking human deliberative reasoning processes.
- Members reflected on the potential to discover new prompting techniques that could significantly influence how models generate responses.
Eleuther Discord
-
nGPT Optimizer Advancements: Boris and Ilya showcased the nGPT optimizer to the Together.AI group, highlighting its performance enhancements based on their expertise and Nvidia's internal findings available on GitHub.
- Feedback from members raised concerns about the reproducibility, computational efficiency, and comparative effectiveness of nGPT compared to existing models.
-
Normalization Techniques in Neural Networks: Yaroslav pointed out that the nGPT paper lacked detailed explanations, leading to flawed implementations, and discussed the potential benefits of using normalization methods like RMSNorm.
- Community members debated the impact of different normalization techniques on model convergence and performance across various neural network architectures.
-
Scaling Pretraining Feasibility: A member asserted that scaling pretraining remains a foundational property of LLMs, emphasizing it is unlikely to become obsolete.
- However, the discussion raised concerns about the economic viability of continued scaling, sparking debates on future resource allocation strategies in pretraining.
-
Function Vectors in In-Context Learning: A paper on function vectors was introduced, exploring how in-context learning (ICL) is influenced by specific attention heads managing tasks such as antonym identification.
- The study concluded that this approach leads to more interpretable task vectors, with an upcoming Arxiv post expected to provide further insights.
-
Few-Shot vs Zero-Shot Evaluation: A user reported an accuracy increase from 52% to 88% in a multiple-choice task when utilizing few-shot evaluations, questioning typical performance metrics in sentiment analysis tasks.
- The conversation highlighted the significance of prompt engineering, with members noting that few-shot strategies can enhance model calibration and reliability.
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) Discord
-
Stable Diffusion 3.5 Optimized for GPU: Users discussed configuring Stable Diffusion 3.5 to run on their GPU by modifying the
sd3_infer.pyfile. A code snippet was shared to set up the working directory and activate the virtual environment.- Proper GPU configuration is essential for performance gains, with emphasis on following the provided setup instructions accurately.
-
Installing diffusers and accelerate for SDXL Lightning: To utilize SDXL Lightning, users were guided to install the
diffusersandacceleratelibraries using a straightforward command. Sample code was provided to demonstrate device settings and inference steps.- Implementing these installations ensures effective image generation, with users appreciating the clear, actionable instructions.
-
Customizing Image Prompts in Stable Diffusion: Users learned how to customize prompts to alter specifics like hair color in image generation commands. Modifying the prompt string directly affects the generated visuals, allowing for creative control.
- This capability enables AI Engineers to fine-tune image outputs to meet precise requirements without altering the underlying model.
-
Roop Unleashed Faces Performance Hurdles: Roop Unleashed users reported prolonged processing times when creating face-swap videos, raising concerns about software efficiency. Discussions highlighted the ongoing challenges with video processing performance.
- Community members are deliberating on potential optimizations to enhance Roop Unleashed's efficiency and reduce processing durations.
-
SDXL Lightning Outperforms SD 1.4: Discussions revealed that SDXL Lightning surpasses older models like SD 1.4 in generating higher-quality images. Users noted the advancements in performance and flexibility with newer models.
- The preference for SDXL Lightning underscores the evolution of stable diffusion models to meet advanced image generation standards.
LM Studio Discord
-
LM Studio Server Accessibility Improved: A user resolved LM Studio Local Server accessibility issues by adjusting firewall settings, switching from
192.168.56.1:2468to192.168.0.100:2468, enabling effective inter-device communication.- This change facilitated seamless server usage across the local network, enhancing productivity and connectivity for users.
-
AI Video Upscaling Tools Compared: Community members evaluated various AI-based video upscaling tools, highlighting Waifu2x for animated content and RealESRGAN for general applications, while noting the high cost of Topaz as a commercial alternative.
- The preference leaned towards free solutions due to their accessibility and effectiveness, fostering discussions on optimizing video quality without significant financial investments.
-
Ubuntu Surpasses Windows in GPU Inference: Ubuntu achieved a GPU inference speed of 375 tokens/sec with a 1b model, outperforming Windows which lagged at 134 tokens/sec, according to recent tests.
- Participants attributed Windows' lower performance to energy-saving power settings and discussed optimizing these settings to enhance GPU efficiency.
-
Nvidia vs AMD GPUs: AI Task Compatibility: Discussions revealed that while the 7900XTX and 3090 offer comparable 24GB VRAM, Nvidia GPUs maintain better compatibility with AI applications due to more robust driver support.
- Conversely, AMD GPUs present challenges with software and driver integration, requiring additional effort to achieve optimal performance in AI tasks.
-
Challenges in Multi-GPU Setups: Users shared plans for extensive multi-GPU setups, including configurations like a 10 RTX 4090 with a Threadripper Pro, aiming for significant performance gains.
- The conversation highlighted complications with mixed GPU brands due to differing driver management systems and raised concerns about shared VRAM efficiency when handling large models.
Nous Research AI Discord
-
Ollama Optimizes Inference with LCPP: Members explored Ollama and its integration with LCPP for efficient inference, highlighting its advantages over traditional frameworks like PyTorch.
- A debate emerged regarding Ollama versus LMStudio, with some users favoring Ollama’s seamless front-end integrations.
-
Hermes 3 Compute Instances Demand High Resources: Discussion centered on the Hermes 3 405 compute instances requiring 8x H100 or 8x A100 80GB nodes, raising concerns about cost-effectiveness.
- Alternative solutions like cloud inference were suggested for budget-conscious scenarios, potentially postponing personal compute expansions.
-
AnyModal Framework Enhances Multimodal Training: AnyModal was introduced as a versatile framework for training multimodal LLMs, enabling the integration of inputs like images and audio via GitHub.
- Members expressed interest in developing demos for image and text interactions, emphasizing streamlined model training processes.
-
LLaMA-Mesh Launches 3D Capabilities: Nvidia unveiled LLaMA-Mesh, leveraging Llama 3.1 8B for 3D mesh generation, with weight releases anticipated soon, as mentioned in Twitter.
- The community received the announcement enthusiastically, recognizing its potential impact on 3D generation technologies.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) Discord
-
Qwen 2.5 Turbo Launch: The Qwen 2.5 Turbo model was introduced with a 1 million token context length and a 4.3x speedup in processing, enhancing its capability to handle larger datasets efficiently.
- This upgrade allows for higher throughput at a competitive price, generating excitement among developers for its potential applications in complex NLP tasks.
-
Mistral AI Pixtral Large Release: Mistral AI unveiled the Pixtral Large model, a multimodal system achieving state-of-the-art results on benchmarks like MathVista, DocVQA, and VQAv2.
- The release also includes enhancements to their chat platform, introducing new interactive tools that improve user engagement and model performance.
-
Deepseek 3 Developments: Anticipation surrounds the upcoming Deepseek 3 release, with discussions hinting at a potential 2.5 VL version that promises advanced model capabilities.
- Community members are optimistic about the enhancements, recognizing the innovative strides made by Chinese models in the AI landscape.
-
RewardBench for RLHF: RewardBench was launched as a benchmark to evaluate reward models in reinforcement learning from human feedback, aiming to refine alignment technologies.
- However, concerns were raised regarding dataset treatment, including accusations of plagiarism against the authors, highlighting the need for ethical standards in benchmark development.
-
LLaVA-o1 Visual Language Model: LLaVA-o1 was announced as a new visual language model outperforming major competitors, featuring a novel inference method that sets it apart in the field.
- Discussions mentioned plans to evaluate its performance against Qwen2-VL, though its availability on Hugging Face remains pending.
Latent Space Discord
-
Pixtral Large Launches Multimodal Prowess: Mistral introduced Pixtral Large, a 124B parameter multimodal model that excels in processing both text and images, accessible via their API and Hugging Face.
- Equipped with a 128K context window and the capability to process up to 30 high-resolution images, it marks a significant milestone in multimodal AI development.
-
Qwen 2.5 Turbo Amplifies Context Handling: Qwen 2.5 Turbo now supports context lengths up to 1 million tokens, enabling extensive text processing comparable to ten novels.
- The model achieves a 100% accuracy rate on the Passkey Retrieval task, enhancing long-form content processing for developers.
-
Windsurf Editor Enhances Developer Workflow: The Windsurf Editor by Codeium integrates AI capabilities akin to Copilot, facilitating seamless collaboration for developers across Mac, Windows, and Linux platforms.
- Its features include collaborative tools and autonomous agents handling complex tasks, ensuring developers remain in a productive flow state.
-
Anthropic API Embeds into Desktop Solutions: The Anthropic API has been successfully integrated into desktop clients, as showcased in this GitHub project.
- Tools like agent.exe enable the AI to generate mouse clicks using pixel coordinates, demonstrating advanced integration capabilities.
-
OpenAI Deploys Streaming for o1 Models: OpenAI has made streaming available for the o1-preview and o1-mini models, broadening access across all paid usage tiers.
- This feature facilitates more dynamic interactions within the OpenAI platform, enhancing the developer experience.
GPU MODE Discord
-
ZLUDA Enables CUDA on Non-NVIDIA GPUs: A recent YouTube video showcased ZLUDA, a tool that provides CUDA capabilities on AMD and Intel GPUs, expanding developer options beyond NVIDIA hardware.
- Community members expressed enthusiasm over Andrzej Janik's appearance in the video, indicating strong interest in leveraging ZLUDA for diverse GPU environments.
-
CK Profiler Boosts FP16 Matrix Multiplication: CK Profiler improved FP16 matrix multiplication performance to 600 TFLOPs, although still trailing the H100's peak of 989.4 TFLOPs as indicated in NVIDIA's whitepaper.
- Performance on AMD's MI300X reached 470 TFLOPs with
torch.matmul(a,b), highlighting the necessity for optimized strategies on AMD hardware.
- Performance on AMD's MI300X reached 470 TFLOPs with
-
Jay Shah's CUTLASS Presentation Highlights FA3: During his talk at CUTLASS, Jay Shah delved into Flash Attention 3 (FA3), discussing column and row permutations to optimize kernel performance without shuffles.
- He emphasized the impact of these permutations on FA3 kernel tuning, prompting members to explore indexing techniques for enhanced GPU computing efficiency.
-
Triton Integrates Modified FlashAttention: A member reported issues while implementing a modified version of FlashAttention in Triton, specifically encountering crashes with
atomic_addin Colab environments.- Efforts are underway to compute the column-sum of the attention score matrix, with community support actively sought to resolve implementation challenges.
-
Advanced PyTorch: DCP and FSDP Enhancements: Discussions around PyTorch's Distributed Checkpoint (DCP) revealed concerns about excessive temporary memory allocation during
dcp.savein mixed precision and FULL_SHARD mode.- FSDP's management of 'flat parameters' necessitates memory for all-gathering and re-sharding, leading to increased memory reservations based on custom auto-wrap policies.
Notebook LM Discord Discord
-
NotebookLM Empowers Content Creators: Former Google CEO Eric Schmidt highlights NotebookLM as his 'ChatGPT moment of this year' for content creation, emphasizing its utility for YouTubers and podcasters in this YouTube video.
- He shares strategies for effective use in creative content generation, showcasing how NotebookLM enhances media production workflows.
-
Seamless RPG Integration with NotebookLM: Users have successfully utilized NotebookLM for RPGs, enabling rapid character and setting creation as demonstrated in Ethan Mollick's experiment.
- A notable member generated a setting and character for their savage worlds RPG in under five minutes, highlighting NotebookLM's efficiency in creative storytelling.
-
Challenges in Audio File Management: Users reported issues with generating separate audio tracks and misnaming audio files upon download in NotebookLM, leading to reliance on digital audio workstations for voice isolation.
- Discussions include potential solutions like employing noise gate techniques to address combined audio file complications.
-
Mixed Usability and Interface Feedback: Feedback on NotebookLM's mobile interface is varied, with users praising its unique capabilities but citing difficulties in navigating and accessing features across devices.
- Users expressed challenges in creating new notebooks and deleting or restarting existing ones, indicating a need for improved interface intuitiveness.
-
Requested Feature Enhancements for NotebookLM: Members have requested features such as RSS feed integration for external information and customizable voice settings without relying on additional applications.
- There are also demands for enhanced support for various file types, including frustrations with uploading formats like XLS and images.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) Discord
-
Mojo Benchmarking with Random Arguments: A user sought advice on performing benchmarking with random function arguments in Mojo but noted that current methods require static arguments, adding undesirable overhead.
- Another user suggested pre-generating data for use in a closure to avoid overhead during benchmarking.
-
Dict Implementation Bug: A user reported a crash occurring when using a Dict with SIMD types in Mojo, which worked up to a SIMD size of 8 but failed beyond that.
- The problem was replicated in a GitHub Issues page, suggesting a deeper issue within the Dict implementation that warrants attention.
-
Exploring Max Graphs for Knowledge Graph Integration: A member pondered whether Max Graphs could effectively unify LLM inference with regular Knowledge Graphs, mentioning their potential use in RAG tools and NeuroSymbolic AI.
- They provided a GitHub link showcasing a proof-of-concept for this approach.
-
MAX's Role in Accelerating Graph Searches: A member questioned if using MAX could aid in accelerating graph search, to which another confirmed the potential but noted limitations.
- It was clarified that unless the entire graph is copied into MAX, current capabilities are limited.
-
Feasibility of Mojo and MAX Implementation: Concerns were raised regarding the feasibility of an agent implemented in Mojo and MAX that infers an LLM to execute searches.
- The idea was met with skepticism, where members debated its practicality in actual application.
Cohere Discord
-
Cohere Model Output Issues: Users have reported odd outputs from the Cohere model, particularly when processing shorter texts, leading to reliability concerns.
- The inconsistent performance has caused frustration, with the model generating bizarre terms and questioning its application suitability.
-
API Reliability Concerns: Multiple users have encountered API errors, including 503 Service Unavailable issues reported on 2024-11-15, indicating potential upstream connection problems.
- These incidents underline ongoing challenges with API availability, prompting users to seek shared experiences and solutions within the engineering community.
-
Developer Office Hours on Long Text: The upcoming Cohere Developer Office Hours on 12:00 pm ET will focus on strategies for handling long text, featuring insights from Maxime Voisin.
- Attendees will explore implementing memory systems in RAG pipelines and discuss use cases like File Upload and SQL Query Generation.
-
Summarization Techniques in RAG Systems: The office hours session will include discussions on compressing and summarizing long text effectively within RAG systems.
- Participants are encouraged to share their use cases and collaborate on strategies to maintain essential information during summarization.
-
Cohere Toolkit Release v1.1.3: The Cohere Toolkit v1.1.3 was released on 2024-11-18, introducing improved global Settings usage and major tool refactoring.
- Key updates include support for ICS files, a File content viewer, and integration enhancements with Azure deployment using Docker compose.
LlamaIndex Discord
-
Python Documentation Enhanced with Ask AI Widget: The Python documentation now includes the 'Ask AI' widget, allowing users to pose questions and receive precise, up-to-date code via a RAG system. Check it out here.
- It’s a truly magically accurate feature that enhances the coding experience!
-
Launch of Mistral Multi-Modal Image Model: Mistral has introduced a new multi-modal image model, available with day 0 support by installing
pip install llama-index-multi-modal-llms-mistralai. Explore its usage in the notebook.- The model supports functions like
completeandstream completefor efficient image understanding.
- The model supports functions like
-
New Multimedia and Financial Report Generators Released: New tools have been released: the Multimedia Research Report Generator showcases generating reports from complex documents visually here, and the Structured Financial Report Generation tool processes 10K documents using a multi-agent workflow, detailed here.
- These tools interleave text and visuals to simplify reporting and analyses.
-
Improvements to CitationQueryEngine and condenseQuestionChatEngine: Users discussed issues with the CitationQueryEngine, such as handling multiple sources, suggesting mapping citation numbers to sources by parsing response text. Additionally, the condenseQuestionChatEngine was reported to generate nonsensical questions when topics abruptly switch, with solutions like customizing the condense prompt and considering CondensePlusContext.
- Implementing these suggestions aims to enhance query coherence and citation accuracy.
-
EY Techathon Team Building and Developer Positions: The EY Techathon team is recruiting, seeking an AI developer and a Web app developer. Interested candidates should DM ASAP to secure their spot.
- Urgent calls for AI and Web app developers emphasize the need for quick action to join the team.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) Discord
-
Liger Kernel Runs 3x Faster: Liger claims to run approximately three times faster than its predecessor while maintaining the same memory usage in worst-case scenarios, with no installation errors reported.
- Some members expressed skepticism, questioning whether this performance boost is exclusive to NVIDIA hardware.
-
AnyModal Framework Integrates Multimodal Data: The AnyModal framework enables the integration of data types like images and audio with LLMs, simplifying setups for tasks such as LaTeX OCR and image captioning.
- Developers are seeking feedback and contributions to enhance the framework, showcasing models like ViT for visual inputs.
-
Chai Research Announces Open-source Grants: Chai, a generative AI startup with 1.3M DAU, is offering unlimited grants ranging from $500 to $5,000 for open-source projects aimed at accelerating community-driven AGI.
- They have already awarded grants to 11 individuals, encouraging developers to submit their projects via Chai Grant.
-
Pretraining and Finetuning Qwen/Qwen2 Models: A member inquired about pretraining the Qwen/Qwen2 model using QLoRA with their pretraining dataset and subsequently finetuning it with an instruct dataset in Alpaca format.
- They confirmed having the Axolotl Docker ready to facilitate the process.
-
Inquiry for vLLM Analytics Platform: A member sought a platform that integrates with vLLM to provide analytics on token usage and enable response inspection.
- This request highlights community interest in tools that enhance monitoring and understanding of vLLM's performance.
tinygrad (George Hotz) Discord
-
Tinygrad Contributions Standards: George emphasized that Tinygrad contributions must meet a high quality standard, stating that low-quality PRs will be closed without comment.
- He advised contributors to review prior merged PRs to align with the project's quality expectations before tackling bounties.
-
Upcoming Tinygrad Release Features: Tinygrad's next release is scheduled in approximately 15 hours, incorporating enhancements such as blocks, lazy buffers, and performance improvements related to Qualcomm scheduling.
- Discussions highlighted the latest updates and their expected impact on the framework's efficiency and functionality.
-
Integration of PyTorch and TensorFlow Methods: The community discussed adding convenience methods like
scatter_add_andxavier_uniformto Tinygrad to reduce repetitive coding efforts.- George agreed to merge these methods from PyTorch and TensorFlow if they are compatible with existing features.
-
Graph and Buffer Management Enhancements: Efforts to refine Big Graph and LazyBuffer concepts are underway, with plans to delete LazyBuffer to improve processing.
- This includes tracking UOp Buffers using WeakKeyDictionary to enhance Tinygrad's performance and functionality.
-
TinyGrad AMD GPU Support without ROCm: A query was raised about whether TinyGrad can train on AMD GPUs without installing ROCm, referencing George's stream where he mentioned ripping out AMD userspace.
- This indicates a potential shift in Tinygrad's GPU support strategy, impacting users with AMD hardware.
LLM Agents (Berkeley MOOC) Discord
-
Exclusive AMA with Intel on AI Development: Join the AMA session with Intel on Building with Intel: Tiber AI Cloud and Intel Liftoff on 11/21 at 3pm PT to gain insights into Intel’s AI tools.
- This event offers a chance to interact with Intel specialists and learn how to enhance your AI projects using their resources.
-
Intel Tiber AI Cloud Capabilities: The session will showcase the Intel Tiber AI Cloud, a platform designed to optimize AI projects with advanced computing capabilities.
- Participants will explore how to leverage this platform for maximum efficiency in their hackathon endeavors.
-
Intel Liftoff Program for Startups: Discussion will focus on the Intel Liftoff Program, which provides startups with mentorship and technical resources.
- Attendees will discover how this program can support their development efforts from inception.
-
Percy Liang's Open-Source Foundation Models: Percy Liang will present on Open-Source and Science in the Era of Foundation Models, emphasizing the importance of open-source contributions to AI.
- Liang will discuss leveraging community support for open-source foundation models, highlighting the need for substantial resources like data, compute, and research expertise.
DSPy Discord
-
DSPy Introduces VLM Support: DSPy recently added support for VLMs in beta, showcasing attributes extraction from images.
- A member shared an example demonstrating how to extract useful attributes from screenshots of websites, highlighting the potential of this feature.
-
Attributes Extraction from Screenshots: The thread discusses techniques for extracting useful attributes from screenshots of websites, indicating practical applications of DSPy.
- This approach aims to streamline how developers can interact with visual data, bringing attention to emerging capabilities in the DSPy toolkit.
-
Less English, More Code in DSPy Signatures: A member shared that most people write too much English in their DSPy signatures; instead, one can achieve a lot with concise code.
- They referenced a tweet by Omar Khattab that emphasizes the effectiveness of super short pseudocode.
-
Tackling Username Generation with DSPy: A user raised concerns about generating diverse usernames, noting that there were many duplicates.
- Another member suggested disabling the cache in the LLM object, but the original user mentioned they had already done so.
-
Increasing Username Randomness with High Variance: To address the issue of duplicate usernames, a member recommended increasing the LLM temperature and adding a storytelling element before the name generation.
- They proposed using a high-temperature model for generating the story and a lower temperature for quality name generation.
LAION Discord
-
Launch of MultiNet Benchmark for VLA Models: The new paper titled "Benchmarking Vision, Language, & Action Models on Robotic Learning Tasks" evaluates VLA models across 20 real-world tasks, revealing key insights about their performance. Full details can be found here.
- This work aims to advance the development of general-purpose robotic systems, demonstrating the critical need for systematic evaluation across diverse tasks.
-
VisRAG Talk at Jina AI: Join the upcoming talk at Jina AI where Shi will explore his innovative work on VisRAG, a fully visual RAG pipeline that eliminates the need for parsing.
- Expect to learn about the construction, evaluation, and future possibilities related to VisRAG, which nearly tripled its training dataset size compared to ColPali.
-
Performance Comparison Among Leading VLA Models: A comparison of GPT-4o, OpenVLA, and JAT shows that while simple tasks like pick-and-place are manageable, models struggle with complex multi-step processes.
- Notably, the results indicate significant performance variations based on the task and robot platform, highlighting the utility of sophisticated prompt engineering with GPT-4o.
-
Introduction of μGATO, a Mini VLA Model: The team introduced μGATO, a mini and understandable baseline model tailored for the MultiNet benchmark, serving as a tool to advance multimodal action models in robotics.
- The ongoing efforts by the Manifold team signal the forthcoming release of more innovations in multimodal action models.
-
Tasty Hacks Hackathon Announcement: A new hackathon, Tasty Hacks, aims to inspire participants to create projects for creativity's sake rather than for utility, moving away from the traditional hackathon culture of optimizing for winning.
- Organizers are seeking kind and nerdy individuals willing to team up and create in a smaller setting of just 20-30 people.
MLOps @Chipro Discord
-
Guidance Needed for MLOps: A member expressed confusion about where to start with MLOps, stating, 'It’s all complicated.'
- Another member requested clarification, asking for more specific concerns, highlighting the need for clearer communication when addressing complex topics like MLOps.
-
Clarification Sought on MLOps Complexity: A member indicated that the question about MLOps was broad and requested more specific details.
- This interaction underscores the necessity for precise communication when tackling intricate subjects like MLOps.
Mozilla AI Discord
-
Pleias launches Common Corpus for LLM training: Pleias, a member of the 2024 Builders Accelerator cohort, announces the release of the Common Corpus, the largest open dataset for LLM training, emphasizing a commitment to having training data under permissive licenses. Find the full post here.
- 'The open LLM ecosystem particularly lacks transparency around training data,' Pleias notes, stating that Common Corpus aims to address this transparency gap.
-
Transformer Lab schedules RAG demo: Transformer Lab is hosting a demo showcasing how to train, tune, evaluate, and use RAG on LLMs without coding, featuring a user-friendly UI. The event promises an easy-to-install process in your local environment, generating excitement in the community. More details.
- Community members are enthusiastic about the streamlined integration of RAG into their workflows.
Torchtune Discord
-
DCP Async Checkpointing Implementation: DCP async checkpointing aims to improve intermediate checkpointing in TorchTune with a new feature that is currently a work in progress.
- This pull request reveals that the process aims to notably enhance efficiency by reducing intermediate checkpointing time by 80%.
-
Intermediate Checkpointing Time Reduction: The implementation of DCP async checkpointing promises significant reductions, estimating an 80% cut in checkpointing time due to improved methodologies.
- This approach is part of ongoing efforts in optimizing distributed checkpointing for better performance.
PART 2: Detailed by-Channel summaries and links
The full channel by channel breakdowns have been truncated for email.
If you want the full breakdown, please visit the web version of this email: !
If you enjoyed AInews, please share with a friend! Thanks in advance!