Sunday, June 15,2025. After No King’s Day. Annette’s Roundup for Democracy.
No Kings Day.
About yesterday.
FYI - “One who recently had pneumonia had to keep her powder dry.” 😩
That was me. Eve went with a neighbor.
I put together this Roundup, to support those protesting and to encourage everyone to join the resistance future protests.
“The celebration of ordinary people who fought against tyranny… [happened] not just in the nation’s capital but all across the country.”
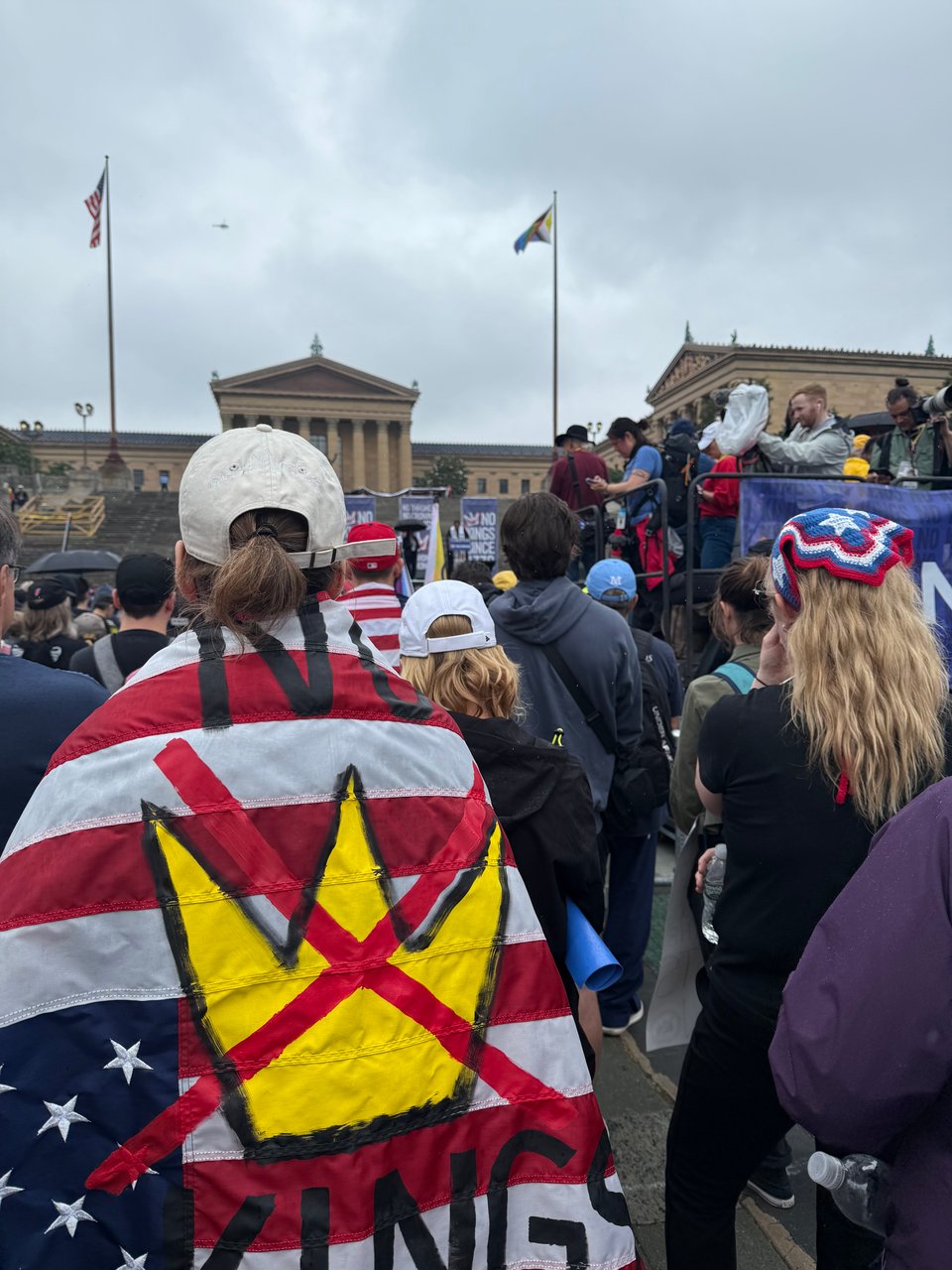

Rev. Dr. William J. Barber II in Philadelphia.
2,000 protests nationally.
New York Times reports-
“Some 2,000 events, organized under the slogan “No Kings,” were planned across all 50 states, animated by the Trump administration’s immigration crackdown, federal spending cuts and Mr. Trump’s military parade in Washington, which coincided with his 79th birthday.”
BREAKING: Dallas, deep red, oil-soaked, and MAGA-aligned is now flooded with anti-Trump protesters. A city once thought untouchable has joined the rebellion. The tide is turning. pic.twitter.com/JwBzxytE5o
— Brian Allen (@allenanalysis) June 14, 2025
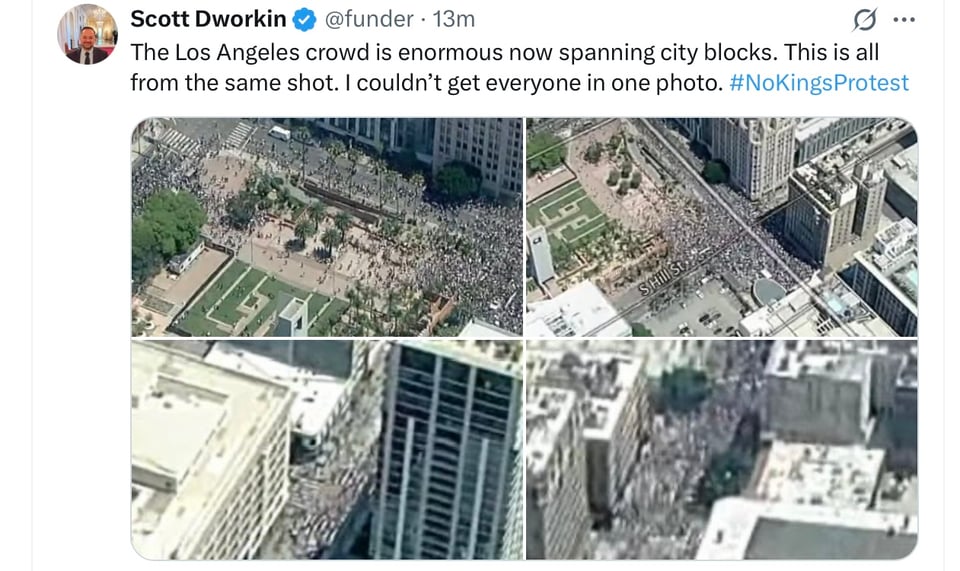
Video shows massive crowd in Downtown Los Angeles protesting against Trump.
— Pop Crave (@PopCrave) June 15, 2025
The ‘No Kings’ protests mark the largest nationwide anti-Trump demonstration since his return to office. pic.twitter.com/evqBcLH4nQ

The United States of America: No Kings since 1776.
— Rep. Jamie Raskin (@RepRaskin) June 14, 2025
Donald Trump: Russian-owned since 1978.
The Guardian says - “Organizers of the “No Kings” Day of Defiance on June 14, 2025 provided a more precise estimate: approximately 5 million people participated across the United States, with 2,000–2,100 individual events in all 50 states.”
The New York Times reports about the protests worldwide - “Protests spread far beyond U.S. cities on Saturday. Videos and images posted to social media showed demonstrators gathering in Spain, England, Sweden, Germany and France, where they sang songs including “The Star-Spangled Banner,” wore patriotic clothing and carried signs. Eunic Epstein-Ortiz, the national spokeswoman for the “No Kings” group, which organized the protests, said there were close to 40 demonstrations across Europe, Africa, Asia and North America. Turnout has been “more overwhelming” than anticipated, Ms. Epstein-Ortiz said.”
Anti Trump protest at Kings Cross in London, UK#NoKingsDay #NoKingsInAmerica pic.twitter.com/m2W212f2Kf
— Piyush Mittal 🇺🇸🇺🇦🇬🇪🇨🇦🟧🌊🌈 (@piyushmittal) June 14, 2025
How we got here.
Heather Cox Richardson, Letters from an American.June 13, 2025

The History.
Two hundred and fifty years ago, on June 14, 1775, the Second Continental Congress resolved “That six companies of expert riflemen, be immediately raised in Pennsylvania, two in Maryland, and two in Virginia; that each company consist of a captain, three lieutenants, four serjeants, four corporals, a drummer or trumpeter, and sixty-eight privates…[and that] each company, as soon as completed, shall march and join the army near Boston, to be there employed as light infantry, under the command of the chief Officer in that army.”
And thus Congress established the Continental Army.
The First Continental Congress, which met in 1774, refused to establish a standing army, afraid that a bad government could use an army against its people. The Congress met in response to the British Parliament’s closing of the port of Boston and imposition of martial law there, but its members hoped they could repair their relationship with King George III and simply sent entreaties to the king to end what were known as the “Intolerable Acts.”
In 1775 the Battles of Lexington and Concord changed the equation. On April 19, British soldiers opened fire on colonists just as Patriot leaders feared they might. In the aftermath of that deadly day, about 15,000 untrained Massachusetts militiamen converged on Boston and laid siege to the town, where they bottled up about 6,500 British Regulars.
The Battles of Lexington and Concord made it clear the British government endangered American liberties. The Second Continental Congress met in what is now called Independence Hall in Philadelphia on May 10, 1775, to address the crisis in Boston. The delegates overcame their suspicions of a standing army to conclude they must bring the various state militias into a continental organization to stand against King George III.
With the establishment of the Continental Army, a British officer, General Charles Lee, resigned his commission in the British Army and published a public letter explaining that the king’s overreach had turned him away from service in His Majesty’s army and toward the Patriots:
“[W]henever it shall please his Majesty to call me forth to any honourable service against the natural hereditary enemies of our country, or in defence of his just rights and dignity, no man will obey the righteous summons with more zeal and alacrity than myself,” he wrote, “but the present measures seem to me so absolutely subversive of the rights and liberties of every individual subject, so destructive to the whole empire at large, and ultimately so ruinous to his Majesty's own person, dignity and family, that I think myself obliged in conscience as a Citizen, Englishman, and Soldier of a free state, to exert my utmost to defeat them.”
After they established a Continental Army, the next thing Congress members did was to name a French and Indian War veteran, Virginia planter George Washington, commander-in-chief. To Washington fell the challenge of establishing an army to defend the nation without creating a military a tyrant could use to repress the people.
It was not an easy project.
The Continental Army was made up of volunteers who were loyal primarily to the officers they had chosen, and because Congress still feared a standing army, their enlistments initially were short. Different units trained with different field manuals, making it hard to turn them into a unified fighting force.
Women came to the camps with their men, often bringing their children. The women worked for the half-rations the government provided, washing, cooking, hauling water, and tending the wounded.
After an initial bout of enthusiasm at the start of the war, men stopped enlisting, and in 1777 Congress increased the times of enlistment to three years or “for the duration” of the conflict. That meant that the men in the army were more often poor than wealthy, enlisting for the bounties offered, and Congress found it easy to overlook those 12,000 people encamped about 18 miles to the northwest of Philadelphia in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania, for six months in the hard winter of 1777–1778. The Congress had no way to compel the states to provide money, food, or supplies for the army, and the army almost fell apart for lack of support.
Supply chains broke as the British captured food or it spoiled in transit to the soldiers, and wartime inflation meant Congress did not appropriate enough money for food. Hunger and disease stalked the camp, but even worse was the lack of clothing. More than 1,000 soldiers died, and about eight or ten deserted every day. Washington warned the president of the Continental Congress that the men were close to mutiny, even as a group of army officers were working with congressmen to replace Washington, complaining about how he was prosecuting the war.
By February 1778 a delegation from the Continental Congress had visited Valley Forge and, understanding that the lack of supplies made the army, and thus the country, truly vulnerable, set out to reform the supply department. Then a newly arrived Prussian officer, Baron Friedrich von Steuben, drilled the soldiers into unity and better morale. And then, in May, the soldiers learned that France had signed a treaty with the American states in February, lending money, matériel, and men to the cause of American independence. The army survived.
By the end of 1778, the main theater of the war had shifted to the South, where British officers hoped to recruit Loyalists to their side. Instead, guerrilla bands helped General Nathanael Greene bait the British into a war of endurance that finally ended on October 19, 1781, at the Battle of Yorktown in Virginia, where British general Charles Cornwallis surrendered to General Washington and French commander Jean-Baptiste-Donatien de Vimeur, Comte de Rochambeau.
The Continental Army had defeated the army of the king and established a nation based on the principle that all men were created equal and had a right to have a say in the government under which they lived.
In September 1783, negotiators concluded the Treaty of Paris that formally ended the war, and Congress discharged most of the troops still in service. In his November 2 farewell address to his men, Washington noted that their victory against such a formidable power was “little short of a standing Miracle.”
“[W]ho has before seen a disciplined Army formed at once from such raw materials?” Washington wrote. “Who that was not a witness could imagine, that the most violent local prejudices would cease so soon, and that Men who came from the different parts of the Continent, strongly disposed by the habits of education, to despise and quarrel with each other, would instantly become but one patriotic band of Brothers?”
With the army disbanded, General Washington himself stepped away from military leadership. On December 23, Washington addressed Congress, saying: “Having now finished the work assigned me, I retire from the great theatre of action, and bidding an affectionate farewell to this august body, under whose orders I have so long acted, I here offer my commission, and take my leave of all the employments of public life.”
In 1817, given the choice of subjects to paint for the Rotunda in the U.S. Capitol, being rebuilt after the British had burned it during the War of 1812, fine artist John Trumbull picked the moment of Washington’s resignation from the army.
As he discussed the project with President James Madison, Trumbull told the president: “I have thought that one of the highest moral lessons ever given to the world, was that presented by the conduct of the commander-in-chief, in resigning his power and commission as he did, when the army, perhaps, would have been unanimously with him, and few of the people disposed to resist his retaining the power which he had used with such happy success, and such irreproachable moderation.”
Madison agreed, and the painting of a man voluntarily walking away from the leadership of a powerful army rather than becoming a dictator hangs today in the Capitol Rotunda.
It is the story of this Army, 250 years old tomorrow, that President Donald J. Trump says he is honoring with a military parade in Washington, D.C., although it also happens to be his 79th birthday.
But the celebration of ordinary people who fought against tyranny will be happening not just in the nation’s capital but all across the country, as Americans participating in at least 2,000 planned No Kings protests recall the principles American patriots championed 250 years ago.
Where we are going.
The '3.5% rule': How a small minority can change the world.
Nonviolent protests are twice as likely to succeed as armed conflicts – and those engaging a threshold of 3.5% of the population have never failed to bring about change.
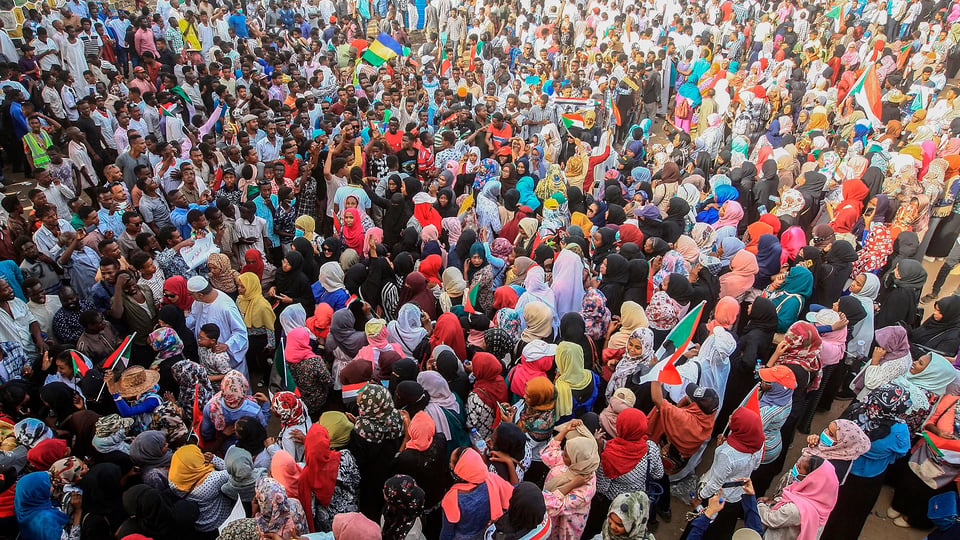

"In 1986, millions of Filipinos took to the streets of Manila in peaceful protest and prayer in the People Power movement. The Marcos regime folded on the fourth day.
In 2003, the people of Georgia ousted Eduard Shevardnadze through the bloodless Rose Revolution, in which protestors stormed the parliament building holding the flowers in their hands."
In each case, civil resistance by ordinary members of the public trumped the political elite to achieve radical change.
There are, of course, many ethical reasons to use nonviolent strategies. But compelling research by Erica Chenoweth, a political scientist at Harvard University, confirms that civil disobedience is not only the moral choice; it is also the most powerful way of shaping world politics – by a long way.
Looking at hundreds of campaigns over the last century, Chenoweth found that nonviolent campaigns are twice as likely to achieve their goals as violent campaigns. And although the exact dynamics will depend on many factors, she has shown it takes around 3.5% of the population actively participating in the protests to ensure serious political change.
Chenoweth’s influence can be seen in the recent Extinction Rebellion protests, whose founders say they have been directly inspired by her findings. So just how did she come to these conclusions?

The organisers of Extinction Rebellion have stated that Chenoweth's work inspired their campaign (Credit: Getty Images).
Needless to say, Chenoweth’s research builds on the philosophies of many influential figures throughout history. The African-American abolitionist Sojourner Truth, the suffrage campaigner Susan B Anthony, the Indian independence activist Mahatma Gandhi and the US civil rights campaigner Martin Luther King have all convincingly argued for the power of peaceful protest.
Yet Chenoweth admits that when she first began her research in the mid-2000s, she was initially rather cynical of the idea that nonviolent actions could be more powerful than armed conflict in most situations. As a PhD student at the University of Colorado, she had spent years studying the factors contributing to the rise of terrorism when she was asked to attend an academic workshop organised by the International Center of Nonviolent Conflict (ICNC), a non-profit organisation based in Washington DC. The workshop presented many compelling examples of peaceful protests bringing about lasting political change – including, for instance, the People Power protests in the Philippines.
But Chenoweth was surprised to find that no-one had comprehensively compared the success rates of nonviolent versus violent protests; perhaps the case studies were simply chosen through some kind of confirmation bias. “I was really motivated by some scepticism that nonviolent resistance could be an effective method for achieving major transformations in society,” she says.
Working with Maria Stephan, a researcher at the ICNC, Chenoweth performed an extensive review of the literature on civil resistance and social movements from 1900 to 2006 – a data set then corroborated with other experts in the field. They primarily considered attempts to bring about regime change. A movement was considered a success if it fully achieved its goals both within a year of its peak engagement and as a direct result of its activities. A regime change resulting from foreign military intervention would not be considered a success, for instance. A campaign was considered violent, meanwhile, if it involved bombings, kidnappings, the destruction of infrastructure – or any other physical harm to people or property.
“We were trying to apply a pretty hard test to nonviolent resistance as a strategy,” Chenoweth says. (The criteria were so strict that India’s independence movement was not considered as evidence in favour of nonviolent protest in Chenoweth and Stephan’s analysis – since Britain’s dwindling military resources were considered to have been a deciding factor, even if the protests themselves were also a huge influence.)
By the end of this process, they had collected data from 323 violent and nonviolent campaigns. And their results – which were published in their book Why Civil Resistance Works: The Strategic Logic of Nonviolent Conflict – were striking.
Strength in numbers
Overall, nonviolent campaigns were twice as likely to succeed as violent campaigns: they led to political change 53% of the time compared to 26% for the violent protests.
This was partly the result of strength in numbers. Chenoweth argues that nonviolent campaigns are more likely to succeed because they can recruit many more participants from a much broader demographic, which can cause severe disruption that paralyses normal urban life and the functioning of society.
In fact, of the 25 largest campaigns that they studied, 20 were nonviolent, and 14 of these were outright successes. Overall, the nonviolent campaigns attracted around four times as many participants (200,000) as the average violent campaign (50,000).
The People Power campaign against the Marcos regime in the Philippines, for instance, attracted two million participants at its height, while the Brazilian uprising in 1984 and 1985 attracted one million, and the Velvet Revolution in Czechoslovakia in 1989 attracted 500,000 participants.
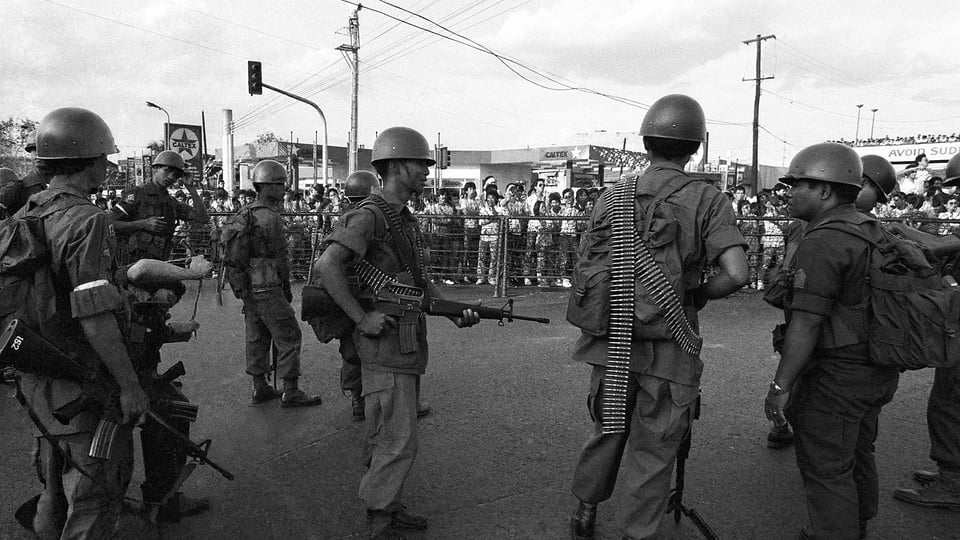

Having attracted millions of supporters, the People Power demonstrations removed the Marcos regime in the Phillipines (Credit: Getty Images)
“Numbers really matter for building power in ways that can really pose a serious challenge or threat to entrenched authorities or occupations,” Chenoweth says – and nonviolent protest seems to be the best way to get that widespread support.
Once around 3.5% of the whole population has begun to participate actively, success appears to be inevitable.
Besides the People Power movement, the Singing Revolution in Estonia and the Rose Revolution in Georgia all reached the 3.5% threshold.
“There weren’t any campaigns that had failed after they had achieved 3.5% participation during a peak event,” says Chenoweth – a phenomenon she has called the “3.5% rule”. Besides the People Power movement, that included the Singing Revolution in Estonia in the late 1980s and the Rose Revolution in Georgia in the early 2003.
Chenoweth admits that she was initially surprised by her results. But she now cites many reasons that nonviolent protests can garner such high levels of support. Perhaps most obviously, violent protests necessarily exclude people who abhor and fear bloodshed, whereas peaceful protesters maintain the moral high ground.
Chenoweth points out that nonviolent protests also have fewer physical barriers to participation. You do not need to be fit and healthy to engage in a strike, whereas violent campaigns tend to lean on the support of physically fit young men. And while many forms of nonviolent protests also carry serious risks – just think of China’s response in Tiananmen Square in 1989 – Chenoweth argues that nonviolent campaigns are generally easier to discuss openly, which means that news of their occurrence can reach a wider audience. Violent movements, on the other hand, require a supply of weapons, and tend to rely on more secretive underground operations that might struggle to reach the general population.
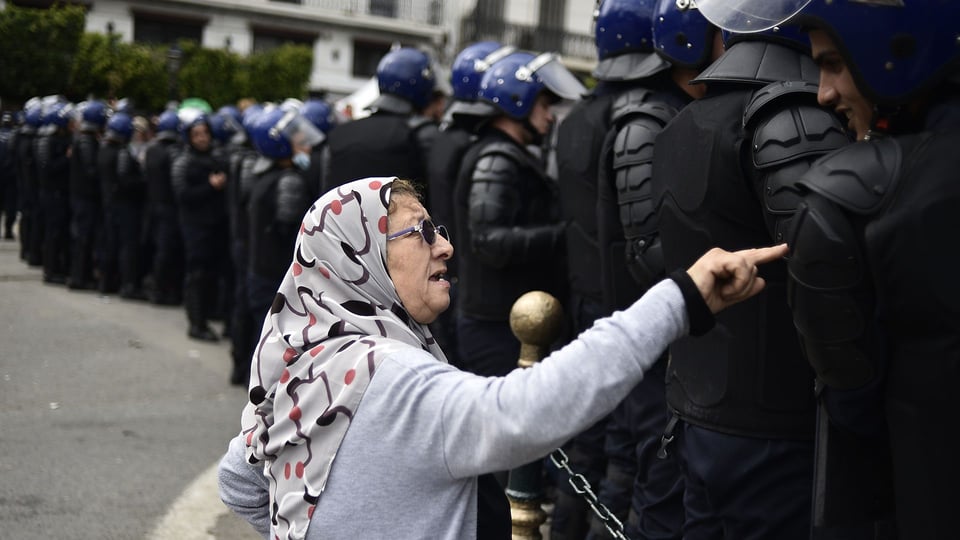

An elderly woman talks to the Algerian security forces during the recent protests (Credit: Getty Images)
By engaging broad support across the population, nonviolent campaigns are also more likely to win support among the police and the military – the very groups that the government should be leaning on to bring about order.
During a peaceful street protest of millions of people, the members of the security forces may also be more likely to fear that their family members or friends are in the crowd – meaning that they fail to crack down on the movement. “Or when they’re looking at the [sheer] numbers of people involved, they may just come to the conclusion the ship has sailed, and they don’t want to go down with the ship,” Chenoweth says.
In terms of the specific strategies that are used, general strikes “are probably one of the most powerful, if not the most powerful, single method of nonviolent resistance”, Chenoweth says. But they do come at a personal cost, whereas other forms of protest can be completely anonymous. She points to the consumer boycotts in apartheid-era South Africa, in which many black citizens refused to buy products from companies with white owners. The result was an economic crisis among the country’s white elite that contributed to the end of segregation in the early 1990s.
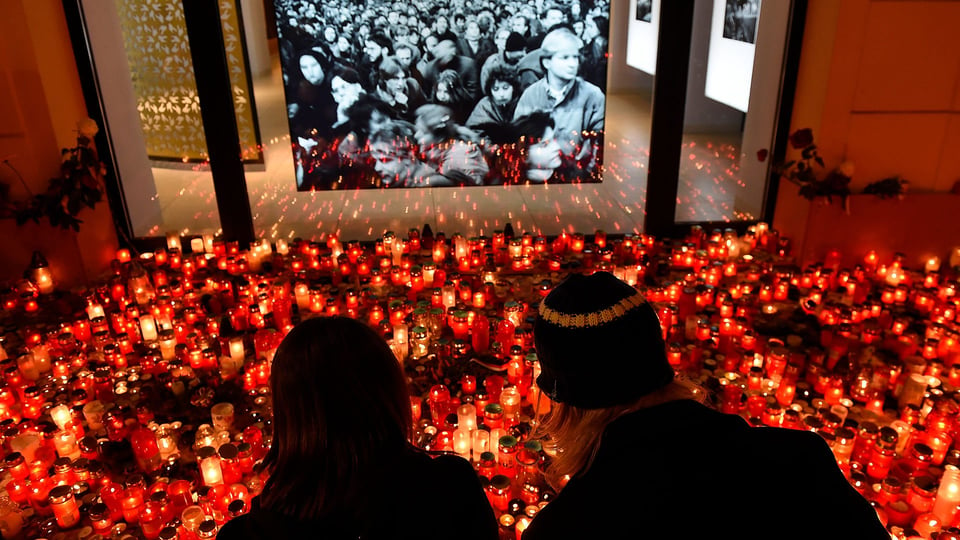

A couple commemorate the Velvet Revolution of 1989, which helped bring down Communist rule in Czechoslovakia - another example of Chenoweth's "3.5% rule" (Credit: Getty Images)
Chenoweth and Stephan’s initial study was first published in 2011 and their findings have attracted a lot of attention since. “It’s hard to overstate how influential they have been to this body of research,” says Matthew Chandler, who researches civil resistance at the University of Notre Dame in Indiana.
Isabel Bramsen, who studies international conflict at the University of Copenhagen agrees that Chenoweth and Stephan’s results are compelling. “It’s [now] an established truth within the field that the nonviolent approaches are much more likely to succeed than violent ones,” she says.
Regarding the “3.5% rule”, she points out that while 3.5% is a small minority, such a level of active participation probably means many more people tacitly agree with the cause.
These researchers are now looking to further untangle the factors that may lead to a movement’s success or failure. Bramsen and Chandler, for instance, both emphasise the importance of unity among demonstrators.
As an example, Bramsen points to the failed uprising in Bahrain in 2011. The campaign initially engaged many protestors, but quickly split into competing factions. The resulting loss of cohesion, Bramsen thinks, ultimately prevented the movement from gaining enough momentum to bring about change.
Chenoweth’s interest has recently focused on protests closer to home – like the Black Lives Matter movement and the Women’s March in 2017. She is also interested in Extinction Rebellion, recently popularised by the involvement of the Swedish activist Greta Thunberg. “They are up against a lot of inertia,” she says. “But I think that they have an incredibly thoughtful and strategic core. And they seem to have all the right instincts about how to develop and teach through a nonviolent resistance campaigns.”
Ultimately, she would like our history books to pay greater attention to nonviolent campaigns rather than concentrating so heavily on warfare. “So many of the histories that we tell one another focus on violence – and even if it is a total disaster, we still find a way to find victories within it,” she says. Yet we tend to ignore the success of peaceful protest, she says.
“Ordinary people, all the time, are engaging in pretty heroic activities that are actually changing the way the world – and those deserve some notice and celebration as well.” (BBC)
One more thing.
No Kings was a good start at 5 million. There will be more protests, and yes, perhaps a national strike.
## Share on social media.
